Unstable market conditions are one of the biggest threats to the success of any company. For decades, managers have used the PESTLE framework to assess the opportunities and risks of their organisation’s macro environment.
Events such as the Brexit referendum or the coronavirus pandemic have had a significant impact on the way companies operate. But even smaller changes such as the introduction of new laws or technologies can pose a significant threat and force companies to react quickly.
If political and macro-economic changes are not recognised by businesses and included in their strategic planning process, attentive competitors can easily take advantage of this shortcoming.
But worry not! Today, you’re going to learn how to analyse your businesses macro environment with the PESTLE framework.
This article will cover:
What is PESTLE Analysis
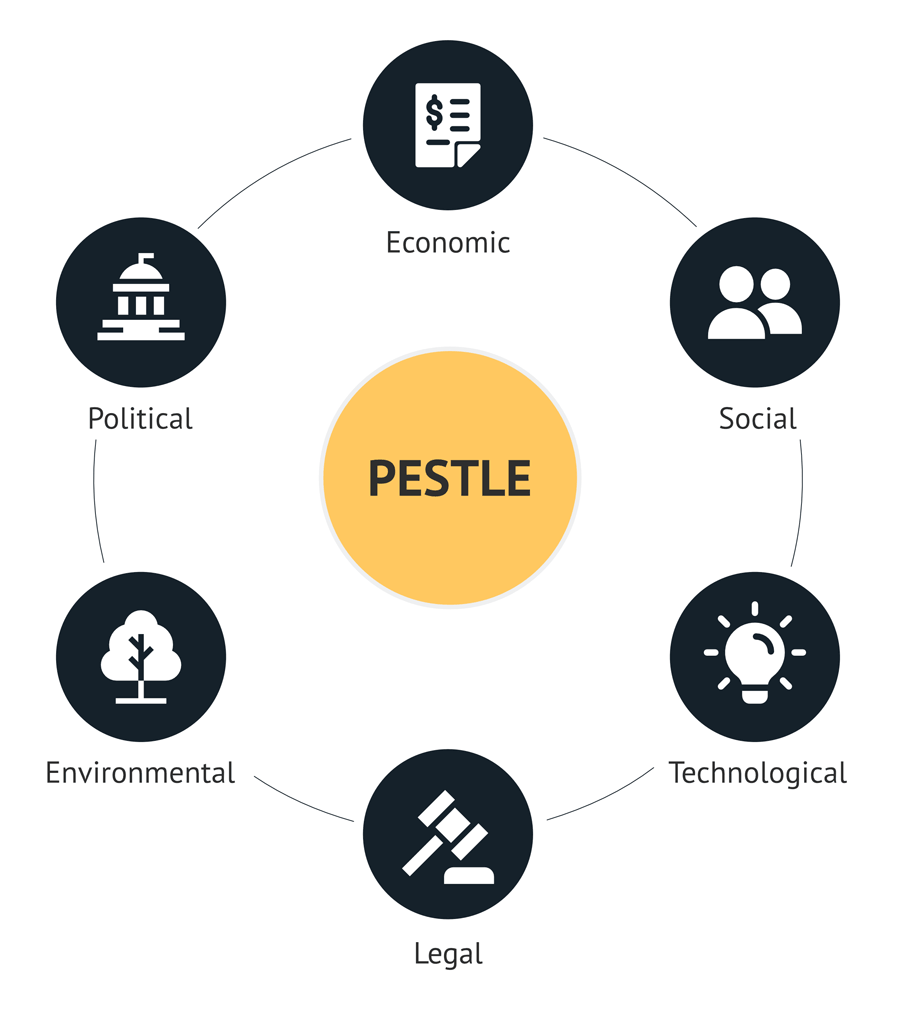
The PESTLE analysis is a concept first mentioned by Harvard Business School professor Francis J. Aguilar. He introduced the framework back in 1964 in his book “Scanning the Business Environment“.
Since then, the PESTLE analysis has become a popular strategic tool to assess the macro environment of organisations worldwide.
The framework categorises the six forces of politics, economics, socio-culture, technology, environment and law.
Political Factors
The PESTLE framework begins with an analysis of the political landscape. That’s because the political stability of a country is probably the biggest priority for any commercial organization.
Unstable conditions or extreme changes in government direction pose a major threat to ongoing operations. They can also lead to a dependency on political goodwill, making it almost impossible to operate economically.
While this is less likely to be the case in democratic states, totalitarian states often have centrally controlled economic systems. These severely restrict any form of business activities or even make them impossible in the first place.
For example, in conflict regions where civil wars prevail, or political power changes are frequent, companies are better off building local distribution networks than setting up nationwide production facilities.
But also relatively stable political conditions can pose challenges:
Take the European Union as an example:
Different legislative, anti-trust, and tax guidelines apply in each country. German domestic and foreign policies will differ widely from the ones in France or Poland.
Organisations need to be aware of the political movements in countries they operate in to minimise the risk of becoming the target of government action.
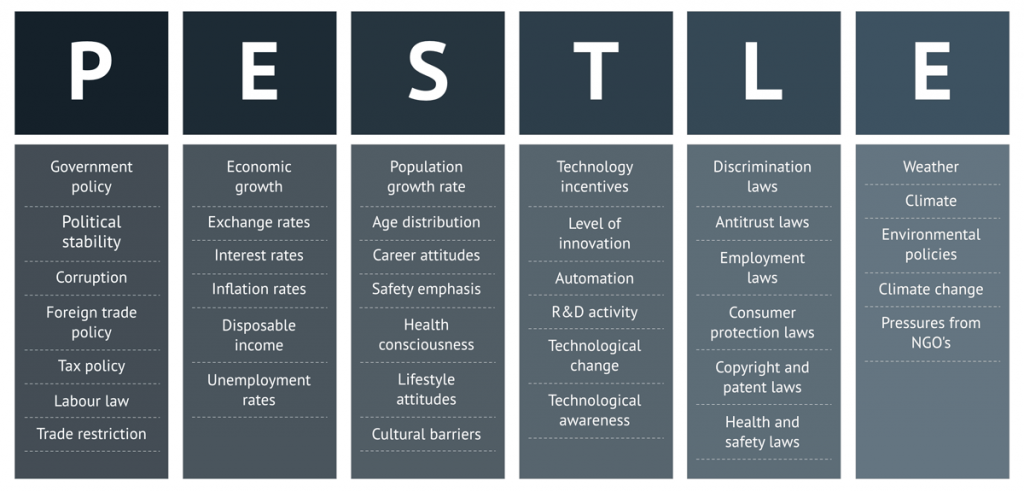
Typical political factors of a PESTLE analysis, include:
- Government policies
- Political stability
- Corruption
- Foreign trade policies
- Tax policies
- Labour laws
- Trade restrictions
Economic Factors
In addition to the political situation, economic aspects play an important role when assessing a company’s macro environment.
The factors to be considered are manifold:
Currency stability, wealth and income distribution, unemployment rates, economic growth rates, wage costs or inflation rates are only a small excerpt of what managers should consider when analysing macroeconomic factors.
These factors can have a direct impact on the growth and profitability of a company.
Before entering a market, decision-makers must ask themselves whether the market is economically attractive and suitable for the intended operation.
Typical economical factors of a PESTLE analysis, include:
- Economic growth
- Exchange rates
- Interest rates
- Inflation rates
- Disposable income
- Unemployment rates
Social Factors
Following on from the economic analysis of a market, the analysis of socio-cultural characteristics provides an insight into the existing values, norms, institutions, education levels and consumption patterns of a population.
Put simply, this information allows businesses to outline the structures and values of a society.
However, managers need to take extra care in this part of the PESTLE analysis:
That’s because they often fall victim to predefined stereotypes when analysing geographically-distant markets.
The socio-cultural factors should always be assessed by several stakeholders with different backgrounds to ensure an objective evaluation of a market.
Typical social factors of a PESTLE analysis, include:
- Population growth rate
- Age distribution
- Career attitudes
- Safety emphasis
- Health consciousness
- Lifestyle attitudes
- Cultural barriers
Technological Factors
In today’s age, almost every company is dependent on modern technologies.
Whether it’s due to the use of digital sales channels or the precise manufacturing of products with modern production facilities.
The rise in technological complexities also increasingly influence strategic decisions in companies.
When assessing environmental factors with the PESTLE framework, decision-makers must consider the technological progress of their time.
Managers can do this by asking a set of questions, like:
- Does the technological progress and infrastructure of a region meet the requirements of the plans to build a new manufacturing plant?
- Do specific technological standards exist with the entry into a new market, which must be met to build an effective supply chain?
- Are there any emerging technologies posing a threat of substitution?
Typical technological factors of a PESTLE analysis, include:
- Technology incentives
- Level of innovation
- Automation
- R&D activity
- Technological change
- Technological awareness
Legal Factors
The legal framework is a central component in the analysis of a company’s macro environment. Even though this area is ranked at the lower end of the PESTLE framework, it is the most important for many companies.
For example, organisations within the EU have to consider at least three legal systems:
- The legislation in the country of the headquarters or production,
- The respective legal system of the country or countries in which the products are sold.
- Additional laws from the European Union that facilitate (or limit) business activities.
These legal systems often deprive managers of the flexibility they seek.
Advertising bans for certain product categories or special requirements for product design must be considered and taken into account on a country by country basis.
The resulting challenges often affect the entire marketing mix and can be costly to solve.
Typical legal factors of a PESTLE analysis, include:
- Discrimination laws
- Antitrust laws
- Employment laws
- Consumer protection laws
- Copyright and patent laws
- Health and safety laws
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors not only assess the climatic and topographical conditions of a country. They also evaluate a country’s availability of resources.
This is important, as products in regions with extreme climatic conditions have to meet different requirements than in their country of origin.
A car in the desert of Dubai has to meet different criteria than in Germany. European carmakers had to adjust their production to ensure their cars would stop catching fire in the UAE, following multiple reports back in 2005.
Geographical distances also pose a challenge for the distribution of products.
Mountains, rivers or other geographical conditions can quickly become a hurdle for transporting raw materials or goods.
Managers must carefully consider whether the ecological-geographical conditions of a region match their organisation’s strategic ambitions.
Typical environmental factors of a PESTLE analysis, include:
- Weather
- Climate
- Environmental policies
- Climate change
- Pressure from NGO’s
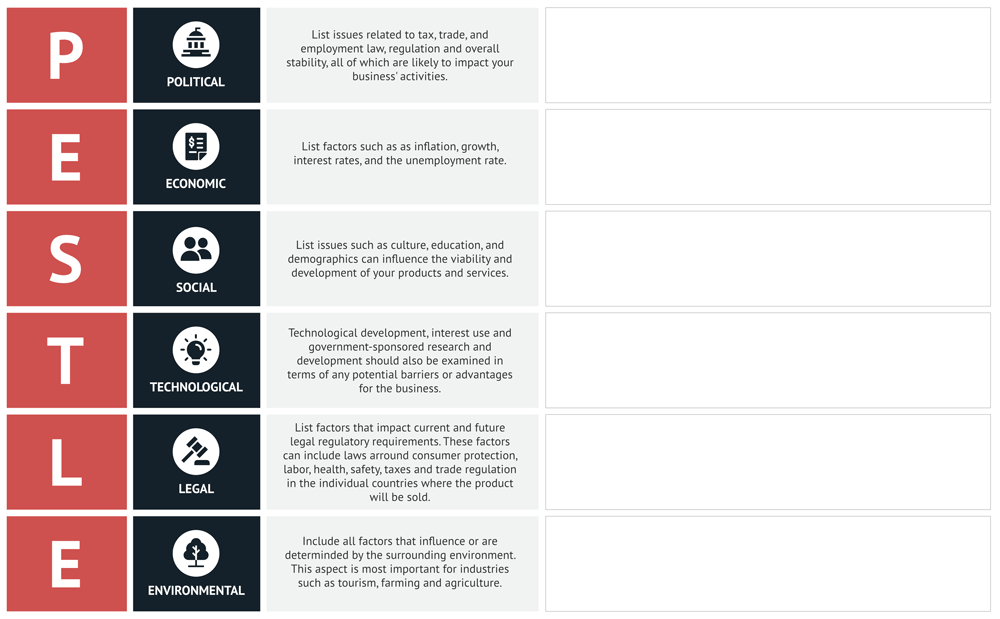
How to do a PESTLE Analysis (Free PDF Template)
Conducting the PESTLE analysis can be overwhelming. But with my easy-to-use template, it becomes a lot more manageable!
Simply print out the below template and start researching your industry.
A couple of great places to start your research are:
Free PESTLE Template
Simply click on the image to get redirected to the high-res PDF.
Conclusion
Over the past decades, the PESTLE Analysis has proven to be an effective concept to assess an organisation’s macro environment.
Its simple setup allows managers to anticipate future business threats and to take action to avoid or minimise their impact by incorporating them into their organisation’s strategic decision-making.
As with any analysis, it reflects the moment and is based on the current knowledge of those carrying it out. That’s why it is recommended to conduct the PESTLE analysis regularly.
Need help analysing your macro-environment?
If you want to better understand the factors that affect your business, get in touch. I offer tailored advice to help you assess your macro environment.
—
Enjoyed this article? Here are more things you might like:
What is Business Strategy? – Increase your chances of success and understand what it takes to build an effective business strategy.
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis – A complete guide to Michael E. Porter’s 5 Forces Analysis to help you assess your competitive landscape.
The Product Life Cycle – A complete breakdown of the individual stages of the product life cycle to plan your next marketing moves.

